Why Are There 64 Codons For 20 Amino Acids: Decoding Genetic Complexity
Why 20 Aminoacids Coded By 64 Codons?
Keywords searched by users: Why are there 64 codons for 20 amino acids there are 64 codons and 20 amino acids which of the following is true, how many codons are codes for amino acids, why are there only 20 amino acids, how many amino acids are there, all codons code for amino acids, how many stop signals are there in the genetic code?, how many different types of amino acids are shown on this codon chart, where is the anticodon located and what is its role in protein synthesis?
What Is The Reason There Are 64 Possible Codons?
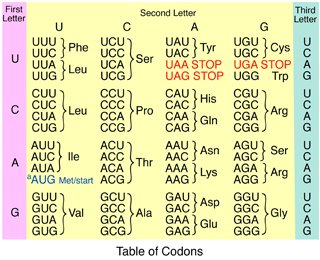
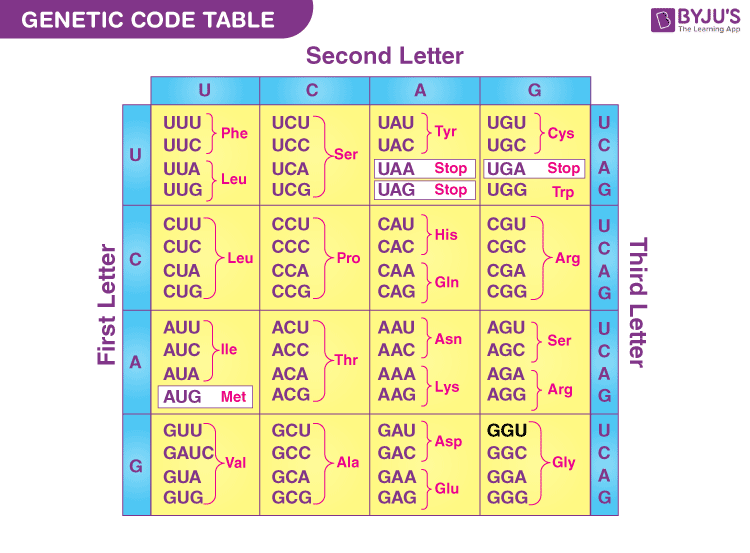
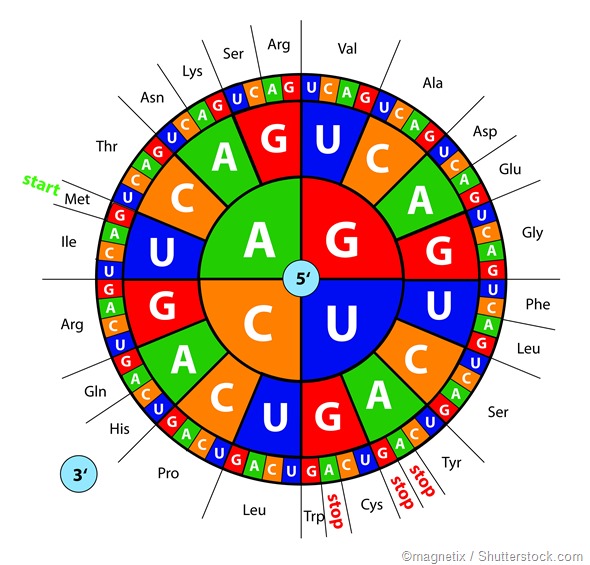
Researchers found that in RNA, a triplet code, also known as a codon, is the smallest combination of nucleotides (A, C, G, and U) that can encode all 20 amino acids. This triplet code consists of three bases, and this choice isn’t arbitrary. It stems from the fact that there are four possible bases at each of the three positions. Therefore, the total number of possible combinations can be calculated by multiplying these options together (4 × 4 × 4), resulting in 64 possible codons. This 64-codon system provides the necessary diversity to encode all the different amino acids required for protein synthesis.
Why Are There 61 Codons That Encode The 20 Amino Acids Instead Of 64?
The genetic code consists of 64 codons, a result of the various combinations of the four nucleic acid bases. This genetic code exhibits a degenerate nature, which means that multiple codons can represent the same amino acid. As a result, out of the 64 codons available, 61 codons have been assigned specific amino acids, encoding the full set of 20 amino acids found in biological proteins. This degeneracy allows for redundancy in the genetic code, providing a degree of robustness against mutations and ensuring the accuracy of protein synthesis.
Which Statement Explains How There Are 64 Codons And Only 20 Amino Acids?
The phenomenon of having 64 codons but only 20 amino acids is known as the degeneracy of the genetic code. To illustrate this concept, let’s consider an example: there are six different codons that can code for three specific amino acids. This alone accounts for 18 out of the 64 possible codon combinations. This concept helps explain the apparent redundancy and versatility of the genetic code, where multiple codons can encode the same amino acid. This principle was first described on September 28, 2015.
Collect 43 Why are there 64 codons for 20 amino acids


Categories: Found 49 Why Are There 64 Codons For 20 Amino Acids
See more here: moicaucachep.com

Because DNA consists of four different bases, and because there are three bases in a codon, and because 4 * 4 * 4 = 64, there are 64 possible patterns for a codon. Since there are only 20 possible amino acids, this means that there is some redundancy — several different codons can encode for the same amino acid.Thus, early researchers quickly determined that the smallest combination of As, Cs, Gs, and Us that could encode all 20 amino acids in RNA would be a triplet (three-base) code. A triplet combination, or codon, would allow for 64 possible combinations (four bases at each of three positions = 4 × 4 × 4 = 64).There are a total of 64 codons in the genetic code arising from the permutation and combination of the 4 bases in nucleic acids. The genetic code is degenerate i.e. more than one codon can code for a single amino acid. Due to this, of the 64 codons, 61 codons code for the 20 amino acids.
Learn more about the topic Why are there 64 codons for 20 amino acids.
- The Big Question – How Cells Work – Science | HowStuffWorks
- Reading the Genetic Code – Nature
- START and STOP Codons – News-Medical.net
- How can there be 64 codon combinations but only … – Socratic
- Deciphering the Genetic Code – National Historic Chemical Landmark
- Codon – National Human Genome Research Institute
See more: https://moicaucachep.com/sports blog